V to Hz 2 click
This device is well suited to be used in a number of various voltage to frequency applications: it can be used in instrumentation applications, industrial, and automation markets. It is well suited for use in AD conversion, long-term integration, linear frequency modulation, voltage-to-frequency conversion and it can be used as the variable clock signal generator. Its function can be complemented by the Hz to V 2 click, which does the opposite type of conversion: frequency into DC voltage. This can be utilized to build an FM modulator/demodulator application, for example.
How does it work?
The main component of the V to Hz 2 click is the VFC32KU, a voltage-to-frequency and frequency-to-voltage converter from Texas Instruments. It accepts voltage at its input and generates a pulse train, with a frequency linearly proportional to the input voltage. The pulse train is routed to a screw terminal labeled as FOUT, as well as the mikroBUS™ INT pin, labeled as FO. The signal can be then further processed by the host MCU.
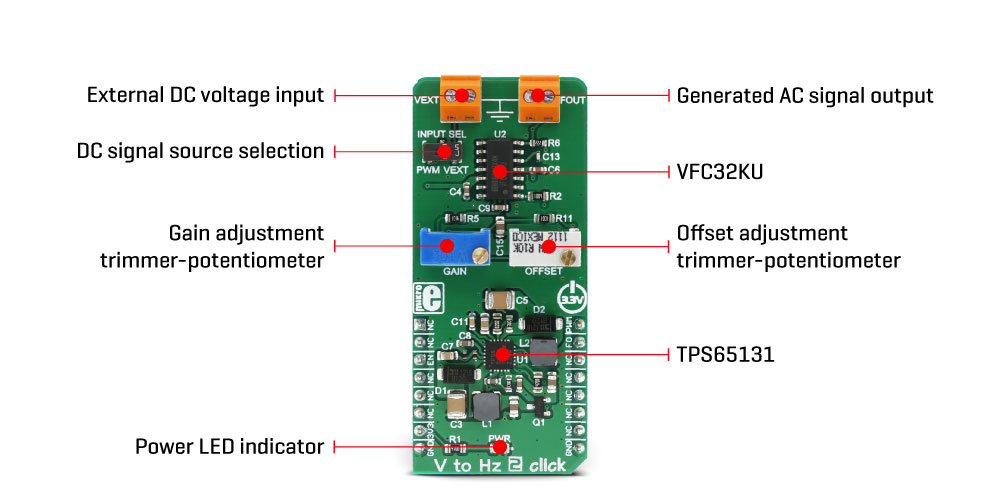
When V to Hz 2 click is operated for the first time, it needs to be calibrated. The click is equipped with two variable resistors for gain and offset fine-tuning. A calibration procedure should be executed before the first use of the Click board™ since even slight variations in the components tolerances could affect the value at the output. It is recommended to correct the offset after longer time intervals, to compensate for the aging of the passive components on the Click board™. It is done by introducing a known voltage at the input, and adjusting the gain and the offset, until the signal with the expected frequency appears on the output.
As already discussed, V to Hz 2 click is equipped with the input voltage terminal (VEXT), which is used to connect the control voltage up to 3.3V. Besides having control voltage input on this terminal, it is possible to select the voltage generated by the MCU as the control voltage input, too. INPUT SEL switch can be set so that the PWM pin from the mikroBUS™ is used as the control voltage input. The PWM signal generated by the MCU is filtered out by the onboard low pass filter so that the control voltage remains constant.
The VFC32KU IC requires a dual power supply with ±15V. Therefore, this Click board™ utilizes another IC in order to provide the required voltages. It uses the TPS65131, a positive and negative output DC/DC Converter, from Texas Instruments. This DC/DC converter has already been used in Boost-INV 2 click, so it was tested "on the field" for this purpose. Providing well-stabilized output with the plenty of power headroom, it is a perfect solution for the V to Hz 2 click, also.
To enable the conversion circuitry, the EN pin of the TPS65131 boost converter should be pulled to a HIGH logic level. This will activate the boost converter and provide the required power for the VFC32KU IC. This pin is routed to the mikroBUS™ CS pin and it is labeled as EN.
Specifications
| Applications | It is well suited for use in AD conversion, long-term integration, linear frequency modulation, voltage-to-frequency conversion and it can be used as the variable clock signal generator |
| On-board modules | VFC32KU, a voltage-to-frequency and frequency-to-voltage converter from Texas Instruments; TPS65131, a positive and negative output DC/DC Converter, from Texas Instruments |
| Key Benefits | V to HZ click features very good linearity, covers a wide frequency range and it has good temperature stability. Onboard high-precision trimmer potentiometers for increased accuracy of the converted pulse train signal, and its frequency persistence |
| Interface | GPIO,PWM |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
Onboard jumpers and settings
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| SW1 | INPUT SEL | Left | Input signal source selection: left position mikroBUS™ FIN pin, right position FEXT input terminal |
| TB1 | FOUT | - | Converted AC voltage output |
| TB2 | VEXT | - | External DC input signal |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on V to Hz 2 click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Software support
We provide a library for the V to Hz 2 Click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
Library initializes and defines GPIO driver and performs commands that can enable or disable the device and get frequency (FOUT) by getting the state of the INT pin. For more details check the documentation.
Key functions :
void vtohz2_enable( uint8_t state )- The function performs enabling and disabling of the device.uint8_t vtohz2_getFreqOut( void )- The function gets the out frequency on mikroBUS INT pin.
Example description
The application is composed of three sections:
- System Initialization - Initializes peripherals and pins.
- Application Initialization - Initializes GPIO driver, performs the device enable and sets the PWM frequency. Also writes help with the possible instructions.
- Application Task - (code snippet) - Checks which command be entered on UART and sets the PWM duty cycle depending on the entered command.
void applicationTask()
{
if (UART_Rdy_Ptr())
{
rxDat = UART_Rd_Ptr();
if ((rxDat == '+') && (percCheck < 100))
{
pwmDutySum += onePercPwm;
percCheck += 1;
}
else if ((rxDat == '-') && (percCheck > 0))
{
pwmDutySum -= onePercPwm;
percCheck -= 1;
}
else if ((rxDat == '*') && (percCheck <= 90))
{
pwmDutySum += tenPercPwm;
percCheck += 10;
}
else if ((rxDat == '/') && (percCheck >= 10))
{
pwmDutySum -= tenPercPwm;
percCheck -= 10;
}
else if (rxDat == 'h')
{
vtohz2_writeHelp();
}
pwmDuty = pwmDutySum;
vtohz2_setSpeed( pwmDuty );
mikrobus_logWrite( "PWM Duty is : ", _LOG_TEXT );
WordToStr( percCheck, text );
mikrobus_logWrite( text, _LOG_TEXT );
mikrobus_logWrite( " %", _LOG_LINE );
}
}
Additional functions :
void vtohz2_writeHelp()- Writes instructions that perform the determined commands.void vtohz2_setSpeed( uint16_t pwm_duty )- Determines the desired PWM duty cycle and checks the limit of the PWM duty.void vtohz2_pwmInit( uint32_t pwm_freq )- Initializes the PWM with the desired frequency and calculates the maximal value of the PWM duty cycle.
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
- Conversions
- PWM
- UART
Additional notes and information
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This click board is supported with mikroSDK - MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant click board demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Downloads
mikroBUS™ Standard specificationV to Hz 2 click: 2D and 3D files
Enter the code in the box below:












