OPTO 4 Click
Featuring very good electrical specifications, including high operating voltage, high current capacity, optical galvanic isolation of the controller circuit, and undervoltage protection, Opto 4 click is a perfect solution which can be used for development of a wide range of power demanding applications, including driving of LED stripes, light bulbs, different types of DC motors, and other similar applications that require an electronically controlled high-current switch.
How does it work?
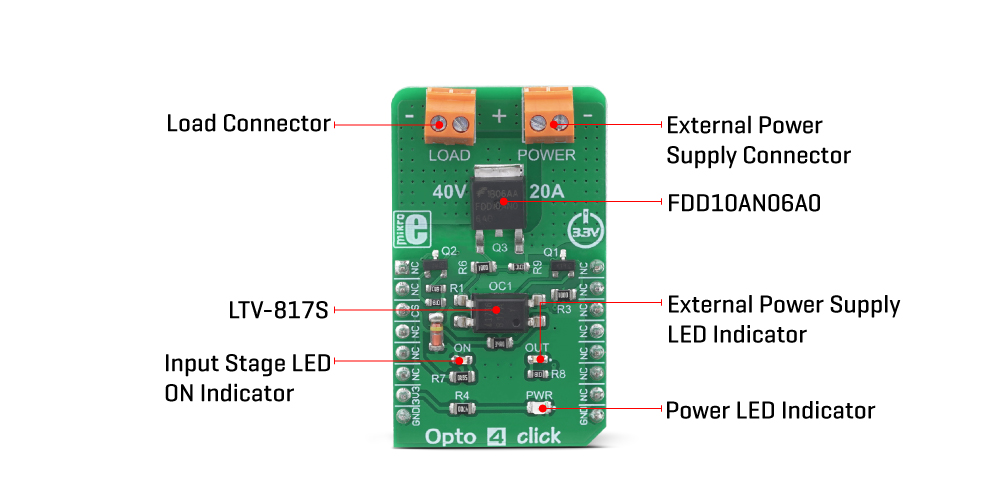
Opto 4 click uses the LTV-817S, an optocoupler with a high isolation voltage, by LITEON. This is a single-channel optocoupler which uses the low current provided by the output pin of the microcontroller (MCU) to activate its output stage. Besides an internal biasing LED, the MCU drives an additional external yellow LED, which signalizes that the MCU output is at a HIGH logic level. This led is labeled as ON, and it is used to indicate the state of the optocoupler output stage (conductive or non-conductive). The host MCU uses the CS pin of the mikroBUS™ to drive the input stage of the LTV-817S optocoupler.
The working principle of an optocoupler is quite simple: A photo-emitting element - usually an IR LED - is integrated on a die along with the photosensitive element, usually a photosensitive transistor. The LED and the photosensitive transistor are isolated galvanically, but not optically: when the internal LED is powered, it emits light, which biases the base of the photosensitive transistor at the output stage, allowing the current to flow through it. In practice, an optocoupler may be equipped with additional elements such as Schmitt triggers, photo-sensitive Darlington pairs, various configurations of MOSFETs, etc.
The output stage of the optocoupler is used to drive the gate terminal of the FDD10AN06A0, an external power MOSFET, manufactured using the PowerTrench® technology, by ON Semiconductor. This MOSFET allows much more current to flow through the connected load, due to its extremely low ON resistance of about 10 mΩ, typically (10V). This MOSFET is designed to be used in switching circuits and for DC/DC converters, providing a high efficiency for these applications. As such, it has a very low capacitance on its gate terminal, allowing it to be driven with reasonably high-frequency PWM signals.
The output stage of the LTV-817S optocoupler is connected to the VIN terminal of the external power supply connector, labeled as POWER. When the output stage of the optocoupler is closed (CS pin of the mikroBUS™ is at a HIGH logic level), it will connect the gate of the power MOSFET to the VIN voltage, thus enabling the power MOSFET. When the output stage of the optocoupler is opened (CS pin is at a LOW logic level), the gate of the MOSFET will be pulled down to the GND, by a 10K resistor, disabling the MOSFET. While enabled, the power MOSFET will be able to conduct the current through an external load, connected to the LOAD terminal. The output stage of the optocoupler also has a green LED indicator labeled as OUT, which indicates that there is a valid voltage level across the POWER terminal.
An undervoltage circuit on the VIN terminal prevents the voltage of the external power supply to drop under 10V. Ideally, the power supply voltage should stay above 12V. It is important for the voltage of the power supply to stay above 10V, since in that case, the ON resistance of the MOSFET is about 10 mΩ, ensuring that no significant heat dissipation will occur as a result of high current through the load. As the voltage of the externally connected power supply drops, it may cause the ON resistance of the power MOSFET to rise enough even before activating the undervoltage circuit (depending on the current through the load), resulting in its damaging. Therefore, the voltage of the external power supply must stay above 10V for this Click board™ to work reliably.
The undervoltage protection feature can be useful to switch off the load in the case when the short-circuit condition occurs: the voltage of the power supply during short circuit event may drop, resulting the undervoltage circuit to be activated. However, if a reasonably strong power supply is used, the short-circuit current may be enough to destroy the power MOSFET or the input terminals.
Specifications
| Type | Optocoupler |
| Applications | Opto 4 click is a perfect solution for development of a wide range of power demanding applications, including driving of LED stripes, light bulbs, different types of DC motors, and other similar applications that require an electronically controlled high-current switch. |
| On-board modules | LTV-817S, a high isolation voltage optocoupler by LITEON; FDD10AN06A0, an external power MOSFET, manufactured using the PowerTrench® technology, by ON Semiconductor. |
| Key Features | Excellent ON resistance of only 10 mΩ, high current conduction capability, high maximum voltage, an undervoltage circuit that ensures the ON resistance of the MOSFET stays within the specified values, etc. |
| Interface | GPIO |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on OPTO 4 Click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| LD2 | ON | - | Input stage ON LED indicator |
| LD3 | OUT | - | External power supply LED indicator |
Software support
We provide a library for the OPTO 4 Click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
The library contains a function for enabling or disabling the output voltage.
Key functions:
void opto4_outputEnable(uint8_t enable)- Function for output enable or disable.
Examples description
The application is composed of the three sections :
- System Initialization - Sets CS pin as OUTPUT.
- Application Initialization - Initialization driver init.
- Application Task - (code snippet) - The Output voltage enable and disable every 3 sec.
void applicationTask()
{
opto4_outputEnable(_OPTO4_OUTPUT_ENABLE);
Delay_ms( 3000 );
opto4_outputEnable(_OPTO4_OUTPUT_DISABLE);
Delay_ms( 3000 );
}
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
GPIO
Additional notes and informations
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
Downloads
mikroBUS™ Standard specificationEnter the code in the box below:










