BarGraph 2 click
BarGraph 2 click is a 10-segment bar graph display click, which uses a high-quality, multicolor bar graph LED display. The bar graph display is a very popular device for displaying various properties, whether it be an audio level, current/voltage level, position of the encoder, and generally any property that can be displayed in a form of a bar graph. The segments of the on-board bar graph LED display are bright and uniformly colored, providing a nice and clean visual feedback.
Each segment is composed of green and red colored LEDs, making it possible to have various important states marked in different color. It can use green, red, and a combination of these two - resulting in having amber colored segments. For example, a VU-meter can have its highest values shown in red (peaks), middle in yellow and the lowest in green; the position of the encoder can be marked with a single red segment, on a green background, and so on. The bar graph display light intensity can be dimmed, by applying a PWM signal. The Click board™ offers a lot of possibilities for building a custom bar graph applications - VU meters, status indicators, various types of gauges, and similar.
How does it work?
When it comes to driving an array of LED segments, using so-called shift register ICs is almost unavoidable. Due to their ability to be connected in cascades, they are commonly used for any type of LED segment array. This Click board™ uses three 74HC595, 8-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift registers with output latches, from Texas Instruments to drive the XGURUGX10D, a 10 segment bar graph array, from SunLED. The 74HC595 ICs are comprised of a D-type internal storage register, as well as the serial-to-parallel shift register, both 8 bits wide. Each of these registers has its own clock line, making it possible to clock in the desired data, and then clock it out to the parallel output pins.
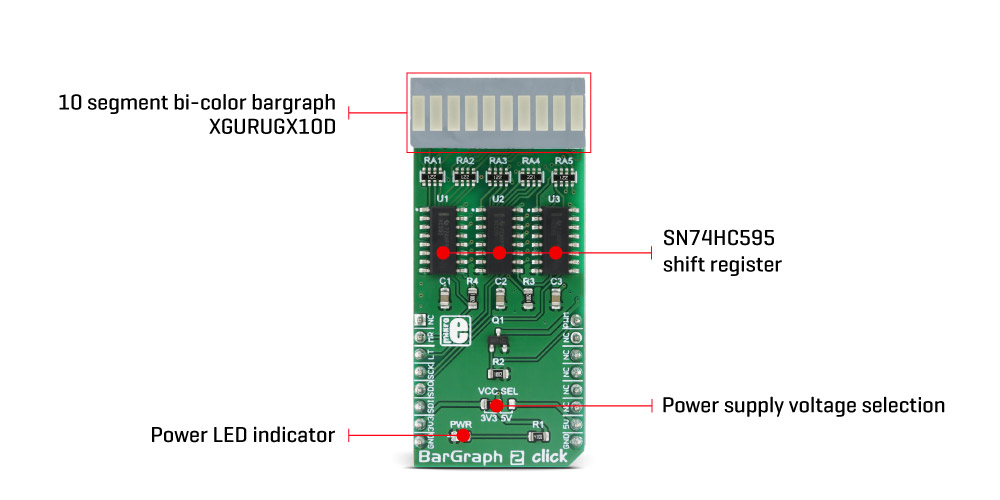
The XGURUGX10D bar graph LED array has 10 dual-color segments. Each segment contains red and green LED, thus having two anodes and one cathode per segment. This results in having 20 LED anodes and 10 LED cathodes, in total. The XGURUGX10D bar graph display is connected as a common cathode type display, meaning that all LED cathodes are routed to a single point. The LED cathode line is connected to the drain of the N channel MOSFET, while its source is connected to the GND. Driving this MOSFET via its gate through the PWM pin of the mikroBUS™ allows dimming of the LED segments. By changing the duty cycle of the PWM signal, it is possible to change the brightness of the XGURUGX10D bar graph display.
The Click board™ communicates with the host MCU via the SPI interface, routed to the mikroBUS™ MOSI, MISO and SCK pins, labeled as SDI, SDO and SCK on this Click board™, respectively. Three bytes of information (24 bits in total) are pushed through the serial data input pin (DS) of the first 74HC595 IC, routed to the SDI pin. The 74HC595 construction is such that after receiving 8 bits, clocking in one more bit will shift the existing 8 bits by one place, overflowing the last bit to the Q7S output pin, shifting it out that way. Since the Q7S of the first 74HC595 is connected to the DS pin of the second 74HC595 (and the Q7S of the second IC is connected to the DS pin of the third 74HC595 IC), clocking in 24 bits to the first 74HC595 IC will fill up all three ICs.
It is worth mentioning that the Q7S of the last 74HC595 IC is routed to the MISO pin of the mikroBUS™, labeled as the SDO, allowing connection of multiple devices in cascade, building more complex setups. Adding more devices in cascade would require more 8bit words to be clocked in the first 74HC595 IC.
The first 10 bits are used to control all the green LEDs of the segments. The second 10 bits are used to control all the red LEDs of the segments. Since the MCU usually clocks out no less than 8 bits through the SPI per cycle, the last 4 bits of the total of 24 bits, are disregarded. When the data has been clocked in, the SPI clock should stop and the CS pin should be driven to a HIGH logic level. The CS pin of the mikroBUS™ is routed to the STCP pin of the 74HC595 ICs, and it is labeled as LT. A rising edge on the STCP input pins of the 74HC595 ICs will latch the data from their internal storage registers to the output pins, polarizing the connected bar graph segment anodes. The STCP pin is pulled to a LOW logic level by the onboard resistor.
The #MR pin is used to clear the data in the internal storage register of the ICs. The LOW logic level on this pin will clear the content of this storage register, but it will not turn off the outputs which are already activated. The #MR pin is routed to the RST pin of the mikroBUS™, labeled as MR and it is pulled to a HIGH logic level by the onboard resistor.
BarGraph 2 click is able to work with both 3.3V and 5V MCUs. The operating voltage selection can be done via the onboard SMD jumper, labeled as VCC SEL.
Specifications
| Type | LED Segment |
| Applications | It can be used for displaying of various signal or status properties, for building VU-meters, and various types of gauges and signal indicators |
| On-board modules | 74HC595, 8-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift registers with output latches, from Texas Instruments; XGURUGX10D, a 10 segment bargraph array, from SunLED |
| Key Features | Clean and bright bargraph dual-color LED display, with uniform light disbursement, simple to use with included software library functions |
| Interface | PWM,SPI |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
| Click board size | L (57.15 x 25.4 mm) |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on BarGraph 2 click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| JP1 | VCC SEL | Right | Power supply voltage selection: left position 3.3V, right position 5V |
Software support
We provide a library for BarGraph 2 click on our Libstock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo application can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Key functions:bargraph2_write(uint8_t regValue);- Generic write functionvoid bargraph2_reset();- Bargraph resetvoid bargraph2_set(uint8_t value);- Sets the bargaph LEDs
Examples Description
- System Initialization - GPIO and SPI module initialization
- Application Initialization - SPI driver initialization
- Application Task - Turning all 10 LED ON sequentially on the bargraph
void applicationTask()
{
for (i = 0; i < 11; i++)
{
bargraph2_set(i);
Delay_ms(100);
}
}
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our Libstock page.
mikroE Libraries used in the example:
- SPI
Additional notes and information
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This click board is supported by mikroSDK - MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant click board demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Downloads
mikroBUS™ Standard specificationLibStock: mikroSDK
XGURUGX10D datasheet
SN74HC595 datasheet
BarGraph 2 click: 2D and 3D files
BarGraph 2 click schematic
Enter the code in the box below:






