Magnetic linear Click
How does it work?
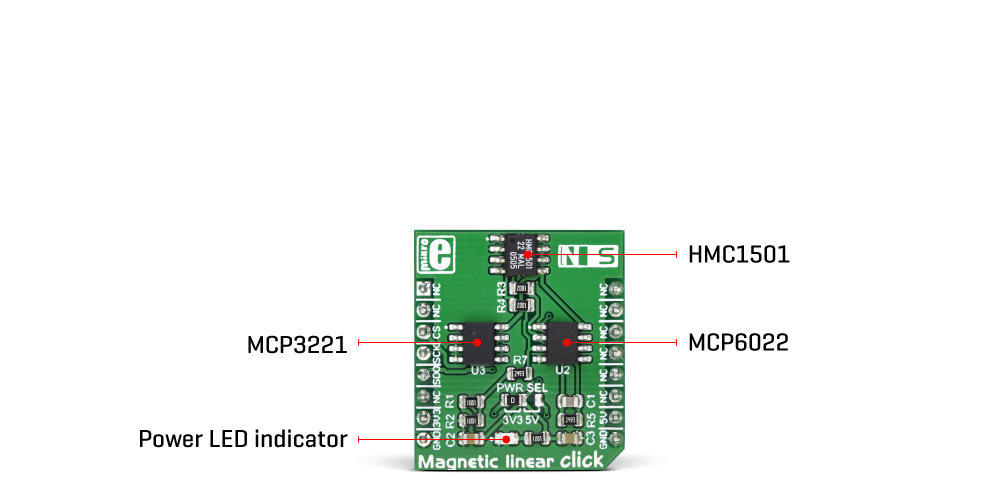
The main component of the Magnetic linear click is the HMC1501, a linear magnetic displacement sensor, from Honeywell. The key feature of the HMC1501 IC is the high accuracy of the magnetic field sensing. Unlike most of the magnetic sensors on the market which rely on the Hall-effect, the integrated sensors of the HMC1501 IC are produced using the Honeywell’s proprietary Anisotropic Magneto-Resistive (AMR) technology, which yields an absolute magnetic position sensing with the angular error of only 0.07° in the range of ±45°. The magneto-resistive sensing elements form a single saturated-mode Wheatstone bridge, positioned in the XZ plane (parallel with the surface of the IC). The IC outputs an analog differential voltage, with respect to the direction of the magnetic field.
The HMC1501 IC is targeted towards working with both bipolar and unipolar single-ended inputs. Each input is labeled as S1 to S8. When a specific channel is selected by using the A0 to A2 pins, it will be switched to the output pin, labeled as D. For the improved stability, each pin is equipped with the 100nF parallel capacitor and 100Ω series resistance. The input and the output signal pins are routed to the standard 2.54mm pitch 2x5 pins header on the Click board™.
- ΔV = -VS · S · sin(2Θ)
Where:
- ΔV is a differential output voltage
- VS is the power supply voltage (3.3V or 5V)
- S is the material constant (12mV/V)
- Θ is the angle of the magnetic field
The outputs of the Wheatstone bridge are routed to the operational amplifier, which serves as the buffer for the A/D converter. For this purpose, only a single channel of the MCP6022, a dual rail-to-rail op-amp from Microchip, is used. This op-amp is biased to half the power supply V and has gain of 25. This buffered signal is then used as the input for the A/D converter.
Magnetic linear click uses the MCP3201, a 12-bit A/D converter (ADC) with the SPI Interface, produced by Microchip. This ADC has a fairly high resolution which can be used even for more demanding applications. At 0°, the ADC will output half of its full-scale (FS) value, and it will swing towards 0 if the sign of the orientation of the magnetic field is positioned towards the negative direction, and 4095 if the orientation of the magnetic field is positioned towards the positive direction. This ADC has the dedicated reference voltage input pin, which is utilized so that the ADC conversion stays within the range of the input signal. The converted output value can be read via the SPI interface, routed to the mikroBUS™ SPI pins for easy interfacing with a vast number of different microcontrollers (MCUs).
The power supply voltage for the whole circuit of the Magnetic linear click can be selected by switching the SMD jumper, labeled as PWR SEL. It offers a selection of the power supply in the range between 3.3V and 5V, available from the mikroBUS™.
Specifications
| Applications | Magnetic linear click can be used for development of various contactless position and direction sensing applications, HMI interfaces, precision measurement applications, proximity detection applications, etc. |
| On-board modules | HMC1501, a magnetic displacement sensor, from Honeywell; MCP6022, a dual, rai-to-rail operational amplifier; MCP3201, a 12-bit A/D converter with SPI interface by Microchip |
| Key Features | A very high precision is achieved by implementing the proprietary Anisotropic magneto-resistive (AMR) technology from Honeywell, absolute sensing of the magnetic field, very compact size, differential outputs from the internal Wheatstone bridge |
| Interface | SPI |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
| Click board size | S (28.6 x 25.4 mm) |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on Magnetic linear click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| J1 | PWR SEL | Left | Power supply voltage selection: left position 3.3V, right position 5V |
Software support
We provide a library for the Magnetic linear click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
TThe library contains a function for reading the linear position of the magnet.
Key functions:
uint16_t magneticlinear_readData()- Functions reads Magnetics Linear data
Examples description
The application is composed of the three sections :
- System Initialization - Initializes SPI init and sets CS pin as OUTPUT
- Application Initialization - Initialization driver init
- Application Task - (code snippet) - Reads Magnetics linear data and this data logs to USBUART every 200ms.
void applicationTask()
{
uint16_t magneticData;
char demoText[ 50 ];
magneticData = magneticlinear_readData();
IntToStr(magneticData, demoText);
mikrobus_logWrite(" Magnetic Linear data : ", _LOG_TEXT);
mikrobus_logWrite(demoText, _LOG_LINE);
mikrobus_logWrite("________________", _LOG_LINE);
Delay_ms( 200 );
}
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
GPIO
Additional notes and information
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
Downloads
mikroBUS™ Standard specificationMagnetic linear click Libstock
Enter the code in the box below:
-228x228.jpg)










