LLC-I2C Click
How does it work?
LLC I2C click does not use an integrated circuit, as already mentioned. With ICs avoided completely, there are some benefits gained: the overall cost of the LLC circuit is greatly reduced, a more robust MOSFET solution reduces the failure rate, and when powered off, both the low voltage and the high voltage sides are isolated from one another (by non-conductive MOSFETs). This type of circuit is sometimes referred to as a level shifting or level translating circuit and it is often necessary when the I2C slave device (typically a sensor IC) uses different logic voltage levels for the I2C communication than the master device, which is a host microcontroller in most cases. The conversion of this circuitry is bi-directional, which makes it suitable to be used with the I2C communication protocol.
The I2C protocol was first introduced by NXP Semiconductors (formerly Philips Semiconductors), in 1982. They also introduced an application note that explains the operation of the LLC circuit in more details. The circuit is divided into low-side and high-side sections for future reference, although the circuit is symmetrical and can be used in both directions.
When there is no communication going on, both gates and sources of the MOSFETs are pulled up to their specific reference voltage levels. This will turn OFF both MOSFETs since there is no gate-source voltage difference (e.g. VG=VS=VSL).
Since the I2C is operated by asserting its bus lines to a LOW logic level, when the source terminal of the MOSFET on one side (e.g. high-side) is driven to a LOW logic level, its VGS potential will rise since the gate voltage is fixed. When the VGS reaches the threshold voltage (1.2V typically for the used transistors), the MOSFET will turn ON, conducting current through the body diode of the opposite-side (low-side) MOSFET, which will become directly polarized. This mechanism can be used to convert signal levels in both directions, within the whole operating range of the used MOSFETs.
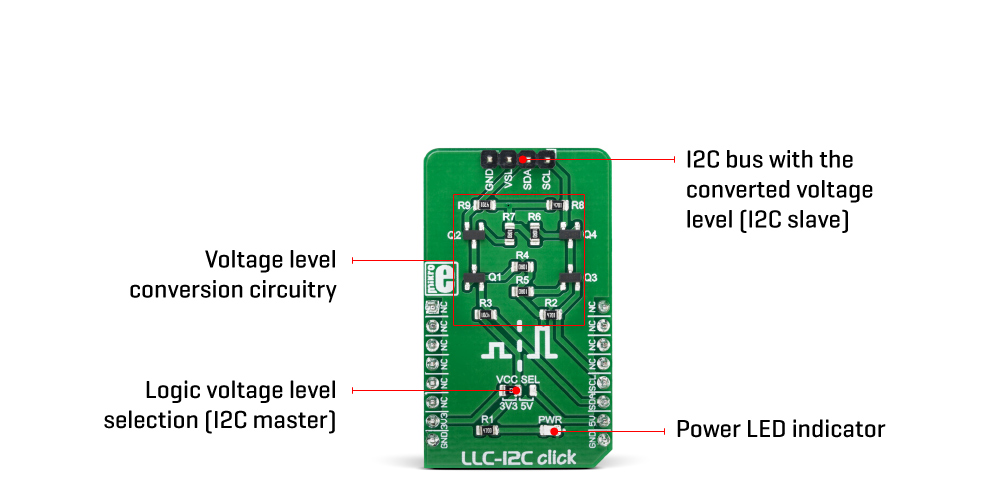
The reference voltage for the high-side can be selected by using the SMD jumper labeled as VCC SEL. The pull-up voltage for the high-side can be selected from the mikroBUS™ power rails, so it can be either 3.3V or 5V. For the low-side, an arbitrary reference voltage can be applied to the VSL pin of the J1 header, respecting the maximum voltage rating. J1 is the standard, 2.54mm pin-header. The low-side I2C bus pins are also routed to the J1 header, allowing an external device to be connected (using the standard wire-jumpers). As already mentioned, the low-side can actually use higher voltage levels than the master, but in most usage scenarios, it will be lower than the master, thus the terminology.
Specifications
| Type | Port expander |
| Applications | The I2C logic level conversion circuit has its application in many different projects, for the logic voltage level matching between the I2C master, and the I2C slave device |
| Key Features | Very low cost achieved using only passive elements, and four MOSFETs, ability to use an arbitrary voltage level conversion in the range from 1.2V up to 10V |
| Interface | I2C |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
| Click board size | M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on LLC I2C Click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PWR | PWR | - | Power LED indicator |
| VCC SEL | VCC SEL | Left | Logic voltage level selection (master): left position 3.3V, right position 5V |
| J1 | - | - | I2C bus with the converted voltage levels (I2C slave) |
Software support
We provide a library for the LLC I2C click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
The library contains functions for starting, writing data to I2C wires and reading data from I2C wires.
Key functions:
void i2cllc_start()- The function executes start condition on I2C wires.
void i2cllc_write(uint8_t slaveAddress, uint8_t *pBuf, uint16_t nBytes, uint8_t endMode)- The function should execute write sequence on I2C wires.
void i2cllc_read(uint8_t slaveAddress, uint8_t *pBuf, uint16_t nBytes, uint8_t endMode)- The function should execute read sequence on I2C wires.
Examples description
The application is composed of the three sections :
- System Initialization - Initializes I2C module
- Application Initialization - Initialization driver init
- Application Task - (code snippet) - Reads the temperature from the Thermo 7 click board and logs data to UART.
Note: The start configuration chip is required at the beginning of each program so that the chip wakes up and prepares for operation and measurement. What is included and set in the start-up function can be viewed in the help file.
void applicationTask()
{
// Thermo 7 measurement Temperature
uint8_t writeReg[ 1 ];
uint8_t readReg[ 2 ] = {0};
float Temp_msb;
uint8_t Temp_lsb;
char tempText[ 50 ];
writeReg[ 0 ] = 0x00;
i2cllc_start();
i2cllc_write( 0x48, &writeReg[0], 1, _I2CLLC_END_MODE_RESTART );
i2cllc_read( 0x48, &readReg[0], 2, _I2CLLC_END_MODE_STOP );
Temp_msb = readReg[ 0 ];
Temp_lsb = readReg[ 1 ] & 0xF0;
if( temp_lsb & 0x80 ) Temp_msb += 0.50;
if( temp_lsb & 0x40 ) Temp_msb += 0.25;
if( temp_lsb & 0x20 ) Temp_msb += 0.125;
if( temp_lsb & 0x10 ) Temp_msb += 0.0625;
FloatToStr(Temp_msb, tempText);
mikrobus_logWrite(" Ambient temperature : ", _LOG_TEXT );
mikrobus_logWrite(tempText, _LOG_TEXT);
mikrobus_logWrite(" C", _LOG_LINE);
Delay_ms( 1000 );
}
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
I2C
Additional notes and information
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This click board is supported with mikroSDK - MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant click board demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Downloads
mikroBUS™ Standard specificationEnter the code in the box below:














