99:1 Metal Gearmotor 25Dx69L mm MP 12V with 48 CPR Encoder
Description
This gearmotor consists of a medium-power, 12 V brushed DC motor combined with a 98.78:1 metal spur gearbox, and it has an integrated 48 CPR quadrature encoder on the motor shaft, which provides 4741.44 counts per revolution of the gearbox’s output shaft. The gearmotor is cylindrical, with a diameter just under 25 mm, and the D-shaped output shaft is 4 mm in diameter and extends 12.5 mm from the face plate of the gearbox. This gearmotor is also available without an encoder.
Key specifications:
| voltage | no-load performance | stall extrapolation |
|---|---|---|
| 12 V | 76 RPM, 200 mA | 12 kg⋅cm (165 oz⋅in), 2.1 A |
Overview
These cylindrical brushed DC gearmotors are available in a wide range of gear ratios and with five different motors (two power levels of 6 V motors and three power levels of 12 V motors). The gearmotors all have the same 25 mm diameter case and 4 mm diameter gearbox output shaft, so it is generally easy to swap one version for another if your design requirements change (though the length of the gearbox tends to increase with the gear ratio). All versions are also available with an integrated 48 CPR quadrature encoder on the motor shaft.
Note: Stalling or overloading gearmotors can greatly decrease their lifetimes and even result in immediate damage. For these gearboxes, the recommended upper limit for instantaneous torque is 200 oz-in (15 kg-cm); we strongly advise keeping applied loads well under this limit. Stalls can also result in rapid (potentially on the order of a second) thermal damage to the motor windings and brushes, especially for the versions that use high-power (HP) motors; a general recommendation for brushed DC motor operation is 25% or less of the stall current.
In general, these kinds of motors can run at voltages above and below their nominal voltages; lower voltages might not be practical, and higher voltages could start negatively affecting the life of the motor.
Details for item #4867
Exact gear ratio: 22×22×22×22×22×23/12×10×10×10×10×10 ≈ 98.78:1
Dimensions
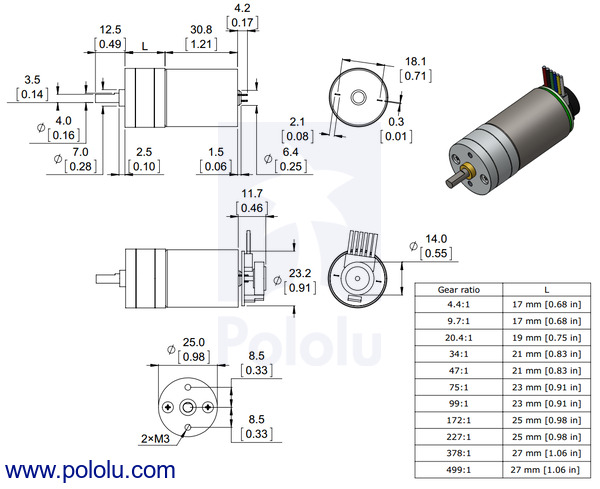
The diagram below shows the dimensions of the 25D mm line of gearmotors (units are mm over [inches]). This diagram is also available as a downloadable PDF (223k pdf).
 |
|
Dimensions of the Pololu 25D mm metal gearmotors. Units are mm over [inches]. |
|---|
Warning: Do not screw too far into the mounting holes as the screws can hit the gears. We recommend screwing no further than 2 mm (0.08″) into the screw hole.
Gearmotor accessories
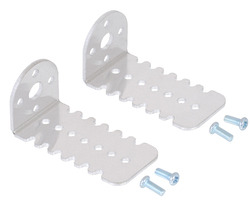
The face plate has two mounting holes threaded for M3 screws. You can use our custom-designed 25D mm metal gearmotor bracket(shown in the picture below) to mount the gearmotor to your project via these mounting holes and the screws that come with the bracket.
|
|
The 4 mm diameter gearbox output shaft works with Pololu universal aluminum mounting hub for 4mm shafts, which can be used to mount our larger Pololu wheels (60mm-, 70mm-, 80mm-, and 90mm-diameter) or custom wheels and mechanisms to the gearmotor’s output shaft as shown in the left picture below. Alternatively, you could use our 4mm scooter wheel adapter to mount many common scooter, skateboard, and inline skate wheels to the gearmotor’s output shaft as shown in the right picture below.
|
|
These are the same type of motors used in the Wild Thumper all-terrain chassis, so the gearbox’s output shaft also works directly with the hex adapters included with the 120mm-diameter Wild Thumper wheels (the left picture below shows a 25D mm gearmotor while the right picture shows the smaller 20D mm gearmotor):
|
|
For a general-purpose hex adapter, consider our 12mm hex wheel adapter, which lets you use this motor with many common hobby RC wheels.
 |
|
12mm Hex Wheel Adapter for 4mm Shaft on a 20D mm Metal Gearmotor. |
|---|
We have a number of motor drivers and motor controllers that work with these 25D mm metal gearmotors. For the LP and MP versions, we recommend our TB9051FTG-based drivers, for which we have a basic single carrier, a dual-channel shield for Arduino, and a dual-channel expansion board for Raspberry Pi. For the HP versions, we recommend our VNH5019-based motor drivers (available as singleand dual carriers), though these can also be a good choice for the lower-power motors.
|
|
If you are looking for higher-level control interfaces, such as USB, RC, analog voltages, I²C, or TTL serial, consider our Simple Motor Controllers, Jrk motor controllers, or RoboClaw motor controllers; these controllers are available in various power levels, and the appropriate one depends on the particular version of 25D mm motor you have (we generally recommend a motor controller that can handle continuous currents above the stall current of your motor).
|
|
|
We have an assortment of Hall effect-based current sensors to choose from for those who need to monitor motor current:
|
|
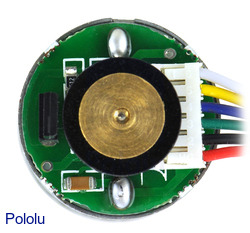 |
|
25D mm metal gearmotor with 48 CPR encoder: close-up view of encoder. |
|---|
Using the encoder (if applicable)
The versions of these gearmotors with encoders use a A two-channel Hall effect sensor to detect the rotation of a magnetic disk on a rear protrusion of the motor shaft. The quadrature encoder provides a resolution of 48 counts per revolution of the motor shaft when counting both edges of both channels. To compute the counts per revolution of the gearbox output, multiply the gear ratio by 48. The motor/encoder has six color-coded, 8″ (20 cm) leads terminated by a 1×6 female header with a 0.1″ pitch, as shown in the main product picture. This header works with standard 0.1″ male headers and our male jumper and precrimped wires. If this header is not convenient for your application, you can pull the crimped wires out of the header or cut the header off. The following table describes the wire functions:
| Color | Function |
|---|---|
| Red | motor power (connects to one motor terminal) |
| Black | motor power (connects to the other motor terminal) |
| Green | encoder GND |
| Blue | encoder Vcc (3.5 V to 20 V) |
| Yellow | encoder A output |
| White | encoder B output |
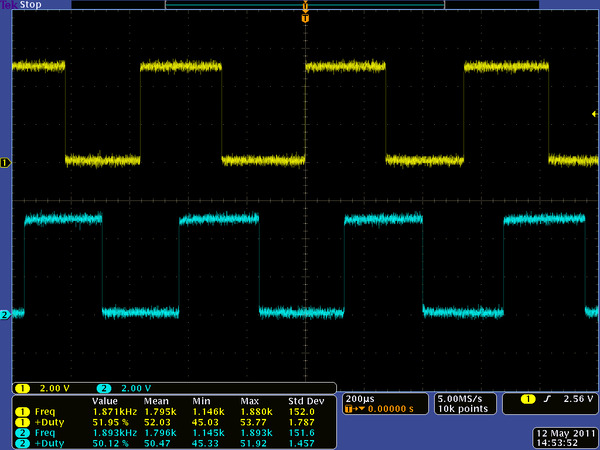
The Hall sensor requires an input voltage, Vcc, between 3.5 and 20 V and draws a maximum of 10 mA. The A and B outputs are square waves from 0 V to Vcc approximately 90° out of phase. The frequency of the transitions tells you the speed of the motor, and the order of the transitions tells you the direction. The following oscilloscope capture shows the A and B (yellow and white) encoder outputs using a motor voltage of 6 V and a Hall sensor Vcc of 5 V:
 |
|
Encoder A and B outputs for 25D mm HP 6V metal gearmotor with 48 CPR encoder (motor running at 6 V). |
|---|
By counting both the rising and falling edges of both the A and B outputs, it is possible to get 48 counts per revolution of the motor shaft. Using just a single edge of one channel results in 12 counts per revolution of the motor shaft, so the frequency of the A output in the above oscilloscope capture is 12 times the motor rotation frequency.
Dimensions
| Size: | 25D x 69L mm1 |
|---|---|
| Shaft diameter: | 4 mm |
General specifications
| Gear ratio: | 98.78:1 |
|---|---|
| No-load speed @ 12V: | 76 rpm |
| No-load current @ 12V: | 200 mA |
| Stall current @ 12V: | 2100 mA |
| Stall torque @ 12V: | 165 oz·in |
| No-load speed @ 6V: | 38 rpm2 |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 1050 mA2 |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 82 oz·in2 |
| Lead length: | 8 in3 |
| Motor type: | 2.1A stall @ 12V (MP 12V) |
| Encoders?: | Y |
Notes:
1. Length measurement is from gearbox face plate to back of encoder cap (it does not include the output shaft). See dimension diagram for details.
2. This motor will run at 6 V but is intended for operation at 12 V.
3. May vary by a few inches.
Enter the code in the box below: